Hospitals worldwide rely heavily on machines and equipment that consume significant amounts of energy to provide essential services to patients. In developing countries like Nigeria, the lack of reliable power supply has contributed to the decay of the health sector. Many hospitals in Nigeria that depend on the national electricity supply face challenges due to poor and unreliable power supply. Those that rely on diesel generators also encounter problems due to high operational costs and maintenance requirements. Unfortunately, power outages have resulted in the loss of patients, and doctors have had to carry out surgeries with torchlights. Embracing new and reliable energy sources is necessary to power health facilities and prevent these unfortunate events. As energy demands continue to rise, businesses are seeking alternative and cost-effective ways to meet their energy needs.
Solar energy has emerged as a viable and sustainable solution to the energy needs of healthcare systems, particularly in resource-constrained settings. Solar energy is renewable, clean, and abundant, and it has the potential to transform the way health care is delivered, particularly in areas with limited or no access to electricity. In this article, we will explore the role of solar energy in improving public health care, including the benefits of solar energy for health care, the challenges of implementing solar energy in health care settings, and the policies and strategies that can support the deployment of solar energy in health care.
Benefits of Solar Energy for Health Care
The healthcare industry plays a vital role in society, providing critical medical services to individuals and communities worldwide. However, healthcare facilities face several challenges, including rising energy costs, limited access to reliable energy sources, and disruptions due to natural disasters. Fortunately, solar energy has emerged as a solution to address these challenges, providing healthcare facilities with a sustainable and cost-effective source of energy. The benefits of solar energy for healthcare are numerous and range from reducing energy costs to improving access to critical medical services in developing nations and supporting disaster relief efforts. Certainly! Here is some additional information on the three main benefits of using solar energy in healthcare:
Reduction of Energy Costs
The cost of energy is a significant factor for healthcare facilities, particularly in low- and middle-income countries where funding is limited. By utilizing solar energy, hospitals and clinics can save money on their energy bills, freeing up resources for other critical needs such as equipment, supplies, and staff salaries. Additionally, since solar panels have a long lifespan and require minimal maintenance, the initial investment in a solar system can lead to long-term savings. Furthermore, solar power can help to stabilize electricity costs since it is not subject to fluctuations in fossil fuel prices.
Improvement of Access to Critical Medical Services in Developing Nations:
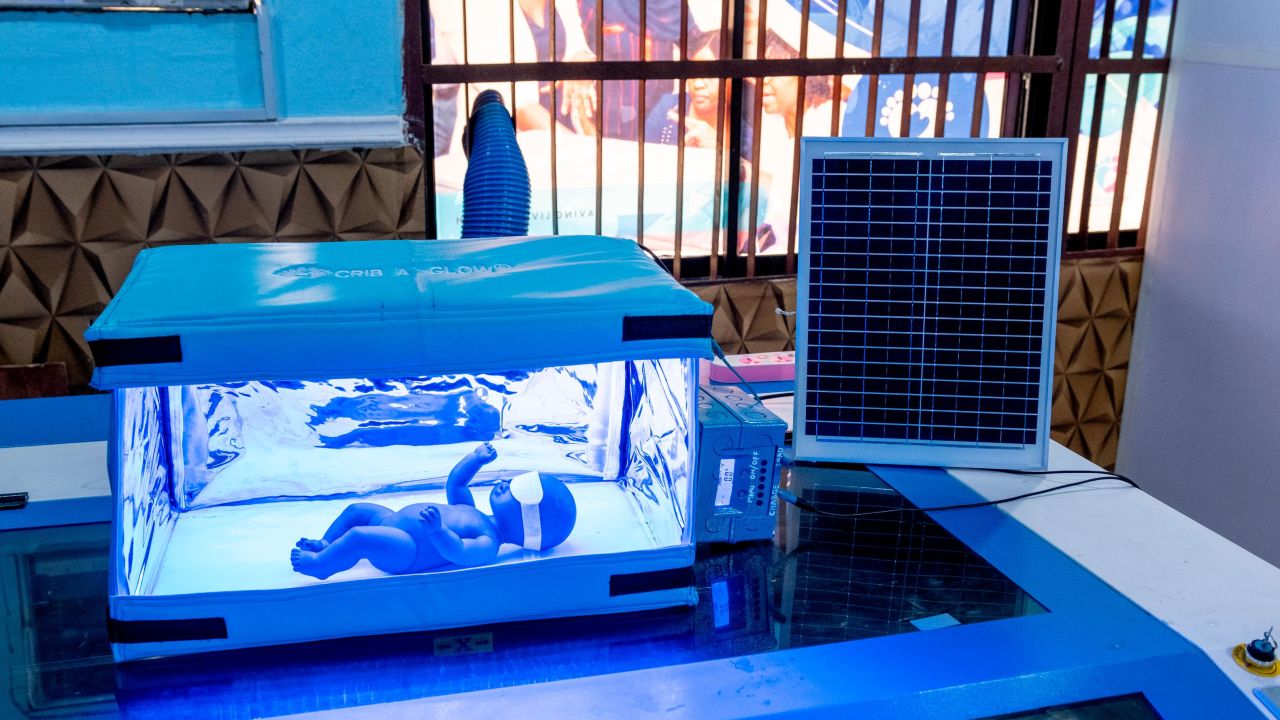

Many healthcare facilities in developing countries lack reliable access to electricity, which can severely impact their ability to provide essential medical services. For example, without power, it is impossible to run life-saving equipment such as ventilators, anaesthesia machines, and diagnostic tools. Moreover, healthcare providers may be forced to work in poorly lit environments or use outdated technology, which can compromise patient care. By implementing solar energy systems, healthcare facilities can overcome these challenges and provide better quality care to their patients.
Support of Disaster Relief Efforts:
Natural disasters such as hurricanes, earthquakes, and floods can wreak havoc on healthcare facilities, disrupting their ability to provide critical care to patients. In such situations, solar-powered technology can serve as a reliable backup source of energy, enabling healthcare providers to continue their work without interruption. Additionally, solar systems can be deployed quickly and are relatively easy to maintain, making them ideal for disaster relief efforts. Furthermore, solar energy is environmentally friendly and does not contribute to air or water pollution, which can be especially beneficial in disaster-stricken areas where clean water and air quality may be compromised.
Challenges of Implementing Solar Energy in Health Care Settings
Despite the benefits of solar energy for health care, there are several challenges to its implementation in health care settings. First, the upfront cost of installing solar energy systems can be high, particularly for small and under-resourced healthcare facilities. The cost of solar panels, batteries, and inverters can be prohibitive for healthcare facilities with limited budgets. In addition, the installation and maintenance of solar energy systems require specialized skills and knowledge, which may not be readily available in some settings.
Secondly, the availability and reliability of solar energy systems can be affected by environmental factors, such as weather patterns and natural disasters. In some areas, solar energy may not be a reliable source of energy due to a lack of sunlight or prolonged periods of cloudy weather. Natural disasters, such as hurricanes, earthquakes, and floods, can also damage solar energy systems and disrupt the supply of energy to healthcare facilities.
Thirdly, the integration of solar energy into healthcare systems requires careful planning and coordination. Healthcare facilities must have the necessary infrastructure to support the installation and maintenance of solar energy systems, including adequate space, wiring, and electrical equipment. In addition, the integration of solar energy systems into health care systems requires the development of appropriate policies and guidelines, as well as the training of health care staff in the use and maintenance of solar energy systems.
Finally, the sustainability of solar energy systems in healthcare settings requires ongoing support and investment. Solar energy systems require periodic maintenance and replacement of components, such as batteries and inverters, which can be costly. Healthcare facilities must have access to funding and technical support to ensure the ongoing maintenance and sustainability of solar energy systems.
Policies and Strategies for Deploying Solar Energy in Health Care
To overcome the challenges of implementing solar energy in healthcare settings, policies and strategies must be developed to support the deployment of solar energy systems. The following are some examples of policies and strategies that can support the deployment of solar energy in public health care:
- Financial incentivesFinancial incentives are a powerful tool that governments can utilize to encourage the adoption of renewable energy sources in healthcare facilities. In particular, solar energy systems are becoming increasingly popular as a sustainable energy source for healthcare facilities due to their long-term cost savings and environmental benefits. The different types of financial incentives that governments can offer include tax breaks, grants, and subsidies.
Tax breaks are one of the most common types of financial incentives offered to healthcare facilities that install solar energy systems. These tax breaks can take the form of credits, deductions, or exemptions, and are designed to significantly reduce the cost of installing solar energy systems. By offering tax breaks, governments can incentivize healthcare facilities to invest in solar energy systems, which in turn can lead to long-term cost savings through reduced energy bills. Grants are another type of financial incentive that governments can offer to healthcare facilities for installing solar energy systems. Grants can help cover the upfront costs of installing solar energy systems, making them more affordable and accessible to healthcare facilities. Additionally, grants can provide financial support for sustainability initiatives, further incentivizing healthcare facilities to invest in solar energy systems.
Finally, subsidies are a form of financial incentive that can be used to offset the cost of installing solar energy systems. These subsidies can take the form of direct payments, discounts on energy bills, or other financial incentives that can make solar energy systems more attractive to healthcare facilities. By offering subsidies, governments can help healthcare facilities become more sustainable and reduce their carbon footprint, while also saving money in the long run through reduced energy bills and increased energy efficiency.
- Capacity building:Capacity building is a critical aspect of the successful adoption and integration of solar energy systems in healthcare facilities. To ensure proper installation, maintenance, and operation of solar energy systems, healthcare staff must have access to the necessary skills and knowledge. Governments can play a vital role in this regard by providing training and capacity-building programs for healthcare staff. These programs can include workshops, seminars, and training sessions focused on the technical aspects of solar energy systems, such as installation, maintenance, troubleshooting, and repair. These programs can also provide information on the benefits of renewable energy sources, energy efficiency, and sustainable practices.
By offering capacity-building programs, governments can empower healthcare facilities to take ownership of their solar energy systems and ensure they are operated efficiently and effectively. This, in turn, leads to better energy management, reduced energy costs, and a smaller carbon footprint. In addition, governments can also provide technical assistance to healthcare facilities, helping them to identify and evaluate the most suitable solar energy systems for their needs. Governments can also facilitate partnerships between healthcare facilities and solar energy providers, fostering collaboration and knowledge sharing.
-
Regulations and Standards:
Developing regulations and standards for the installation and operation of solar energy systems in healthcare settings is essential to ensure the safety, reliability, and efficiency of these systems. Governments play a vital role in this regard by establishing guidelines and regulations that healthcare facilities must adhere to when installing and operating solar energy systems. Regulations can cover a range of aspects related to solar energy systems, such as installation, maintenance, safety, and performance standards. By setting minimum requirements for solar energy systems, governments can ensure that healthcare facilities are installing reliable and safe systems that meet performance expectations. These regulations can also help ensure that healthcare facilities are following proper procedures for installation and maintenance, reducing the risk of accidents or malfunctions.
Standards can also play an essential role in the successful integration of solar energy systems in healthcare settings. Standards can provide guidelines for the design, installation, operation, and maintenance of solar energy systems, ensuring that they are compatible with existing healthcare systems and meet performance expectations. Standards can also promote uniformity in the installation and operation of solar energy systems, making it easier for healthcare facilities to adopt and integrate these systems. By developing regulations and standards for the installation and operation of solar energy systems in healthcare settings, governments can promote the adoption of renewable energy sources while ensuring the safety and reliability of these systems.
-
Public-private partnerships:
Public-private partnerships can provide a mechanism for the deployment of solar energy systems in healthcare settings. Private sector companies can provide the necessary financing, technical expertise, and support for the installation and maintenance of solar energy systems, while governments can provide policy and regulatory support.
Conclusion
The deployment of solar energy in healthcare settings has the potential to transform the way healthcare is delivered, particularly in resource-constrained settings. Solar energy is renewable, clean, and abundant, and it can provide reliable and affordable energy to healthcare facilities, even in remote and off-grid areas. The benefits of solar energy for health care are significant, including improved health outcomes, reduced operational costs, and improved quality of health care services. However, the implementation of solar energy in healthcare settings requires careful planning and coordination, as well as the development of appropriate policies and strategies. Governments and other stakeholders must work together to support the deployment of solar energy in healthcare settings and ensure the sustainable and effective use of this important resource.

